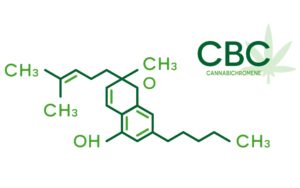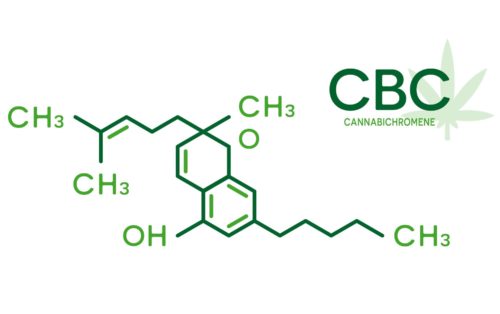
Cannabichromene (CBC) is a phytocannabinoid found in marijuana. This compound has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. It also stimulates the CB2 receptors and inhibits the growth of cancer cells. The benefits of CBC are numerous, and many people are starting to use it in their daily routines.
It has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
Cbc products may help you reduce acne and soothe a range of conditions. They work by reducing excessive oil production on the skin and have antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. They may also help treat respiratory problems. In addition, some people use CBC for various reasons, including relaxation and stress relief.
CBC has anti-inflammatory properties and has been shown to inhibit the formation of nitric oxide and limit the destructive capacity of macrophages. In experiments, CBC was found to limit the destruction of intestinal tissues in experimental murine colitis. Further research is required to explore whether CBC has a role in fighting intestinal inflammation in humans.
CBC has strong antibacterial properties and is effective against many strains of bacteria and fungi. It also has antifungal properties.
CBC is also beneficial for acne and may promote bone growth. In addition, the anti-inflammatory properties of CBC make it a good candidate for pain relief. Moreover, the non-psychoactive nature of this compound makes it a great option for treating acne. There are a wide variety of products to choose from if you are looking for a CBC-based product.
It stimulates CB2 receptors
CBC is a phytocannabinoid that stimulates CB2 receptors and has a broad spectrum of therapeutic and anti-inflammatory effects. However, more research is needed to understand the mechanism of CBC’s action fully. CBC works through GPCR kinases responsible for ions passing between cell membranes. In addition, it also enhances the levels of natural endocannabinoids in the body.
CB2 receptors regulate synaptic function and have been implicated in drug abuse. They also regulate inhibitory plasticity in the CA2/3 regions of the hippocampus. In addition, they are thought to control gamma oscillations in vivo. Unlike their CB1 counterparts, CB2 receptors are neuronal in origin and act independently of CB1 receptors.
The amount of CBC present on the surface of CB2 cells is not a significant factor in their activation.
It inhibits the growth of new cancer cells
In 2006, a published study suggested that CBC products may potentially inhibit the growth of new cancer cells. However, that study focused on cannabinoids other than THC, the psychoactive ingredient found in marijuana. While THC is known to have anti-tumor properties, its psychotropic nature makes it difficult to use in a conventional chemotherapy regimen.
Scientists have found that cannabinoids in cannabis inhibit inflammation and tumor growth. One of these compounds, anandamide, has been shown to fight breast cancer. Other cannabinoids may eventually be used as chemopreventives. But for now, researchers are just beginning to learn how these compounds can help us fight cancer.
Cannabichromene (CBC) is a phytocannabinoid found in marijuana.
Cannabichromene is a phytocannabinoid that has a unique set of pharmacological properties. The compound inhibits the uptake of anandamide, an endogenous cannabinoid that regulates appetite and mood. CBC may also affect these functions indirectly through its interaction with transient receptor potential cation channels.
CBC is a naturally-occurring phytocannabinoid that is found in marijuana. It has antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory properties and is believed to be the second-most abundant cannabinoid in the plant. While cannabichromene is not psychoactive, it has been found to have several beneficial effects on humans and rodents.
Studies have found that cannabichromene has an antidepressant-like effect in animals.
Cannabichromene inhibits nitric oxide production and has anti-inflammatory properties. These properties are useful in fighting inflammatory conditions such as osteoarthritis. Researchers have also shown that cannabichromene is an antibacterial agent that inhibits bacterial growth. CBC is a promising candidate for further research.
Cannabichromene is thought to interact with the ECS, the part of the body that controls pain. It may also act as an agonist for the TRPV1 and TRPA1 receptors, responsible for controlling body temperature and pain. CBD and CBC interact with the CB1 and CB2 receptors in the brain. Moreover, they may enhance the production of endocannabinoids in the body.